Rétroéclairage
Les rétroéclairages sont principalement divisés en trois types en fonction de la source lumineuse : LED, CCFL et EL. En fonction de leur emplacement de distribution, ils sont en outre classés en panneaux de rétroéclairage à éclairage périphérique et à éclairage direct. Ce qui suit est une brève introduction. Dans le domaine du rétroéclairage LED, nous proposons depuis longtemps à nos clients des solutions de rétroéclairage LED personnalisées, en optimisant l'agencement des plaque de guidage de lumière (LGP) et des sources lumineuses pour améliorer les performances d’affichage et réduire la consommation d’énergie.
1. Rétroéclairage LED
Les lampes LED, également connues sous le nom de diodes électroluminescentes, ont la consommation d'énergie par unité la plus faible par rapport aux autres sources lumineuses. Les lumières LED sont disponibles en différentes couleurs, du bleu au rouge. Il existe également une couleur spéciale appelée blanc. Parmi les différentes couleurs, elles peuvent être largement classées en types de luminosité élevée et faible.
Le blanc étant une couleur mixte sans valeur de longueur d’onde identifiable, il est représenté par ses coordonnées sur le diagramme de chromaticité. Nous l’avons défini comme « blanc froid » et « blanc chaud ». Des problèmes de déviation de couleur existent dans toutes les couleurs, le bleu et le blanc étant particulièrement visibles, en particulier le blanc, que même les fournisseurs de LED ne peuvent pas contrôler efficacement.
Rétroéclairage LED éclairé par les bords :
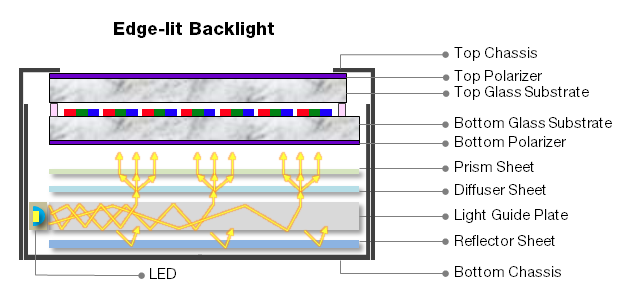
Cela implique de placer des sources lumineuses linéaires ou ponctuelles le long des côtés d’une plaque de guidage de lumière spécialement conçue pour créer un rétroéclairage. En fonction des besoins réels d'utilisation, il peut également être réalisé en version double face, voire triple face. Les rétroéclairages éclairés par les bords peuvent généralement être très fins, mais le taux d'utilisation de la lumière de la source lumineuse est relativement faible, et plus elle est fine, plus le taux d'utilisation est faible, avec un maximum d'environ 50 %. La technologie de base réside dans la conception et la fabrication de la plaque de guidage de lumière.
Rétroéclairage LED à éclairage direct :
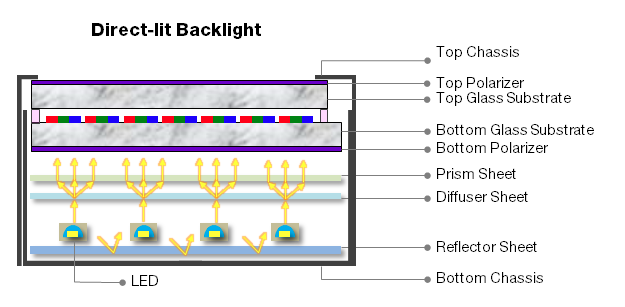
Les LED sont uniformément disposées sous le panneau d’affichage. Les avantages incluent une bonne luminosité et une bonne uniformité. Les inconvénients incluent une plus grande épaisseur (plus de 4,0 mm), une utilisation plus élevée des LED et une génération de chaleur notable. Les conceptions utilisent généralement des couleurs à faible luminosité, tandis que les couleurs à haute luminosité sont rarement prises en compte en raison de contraintes de coût.
Une source de lumière électrique fait référence à un dispositif ou un appareil qui convertit l'énergie électrique en énergie lumineuse. Il est largement utilisé dans l’éclairage quotidien, la production industrielle et agricole, la défense nationale et la recherche scientifique.
2. Rétroéclairage EL
L'électroluminescence (EL) est une source de lumière froide qui émet de la lumière grâce à la luminescence intrinsèque de phosphores excités par un champ électrique alternatif. Son premier avantage est sa finesse, avec une épaisseur allant de 0,2 à 0,6 mm. Les inconvénients incluent une faible luminosité, une courte durée de vie (généralement de 3 000 à 5 000 heures), la nécessité d'une alimentation électrique pilotée par un onduleur et une sensibilité aux interférences des circuits, qui peuvent provoquer des scintillements et du bruit. Le rétroéclairage EL peut être piloté par des onduleurs ou des circuits intégrés pilotes. Cependant, étant donné que la fréquence et la tension de sortie de charge des circuits intégrés de pilotage ne répondent pas aux exigences typiques des EL (400 Hz, 100 V CA), leur luminosité est inférieure à celle des systèmes pilotés par onduleur. Des rétroéclairages EL et LCD à lumière blanche (en couleur) ont également fait leur apparition.
Application: cependant, en raison de leur faible luminosité, ils sont principalement utilisés dans les écrans LCD de petite taille de moins de 4 pouces, tels que les téléphones mobiles, les PDA et les consoles de jeux. Pour les rétroéclairages couleur (lumière blanche) et de grande taille à haute luminosité, la solution principale reste l'utilisation du CCFL comme source de lumière.
3. Rétroéclairage CCFL
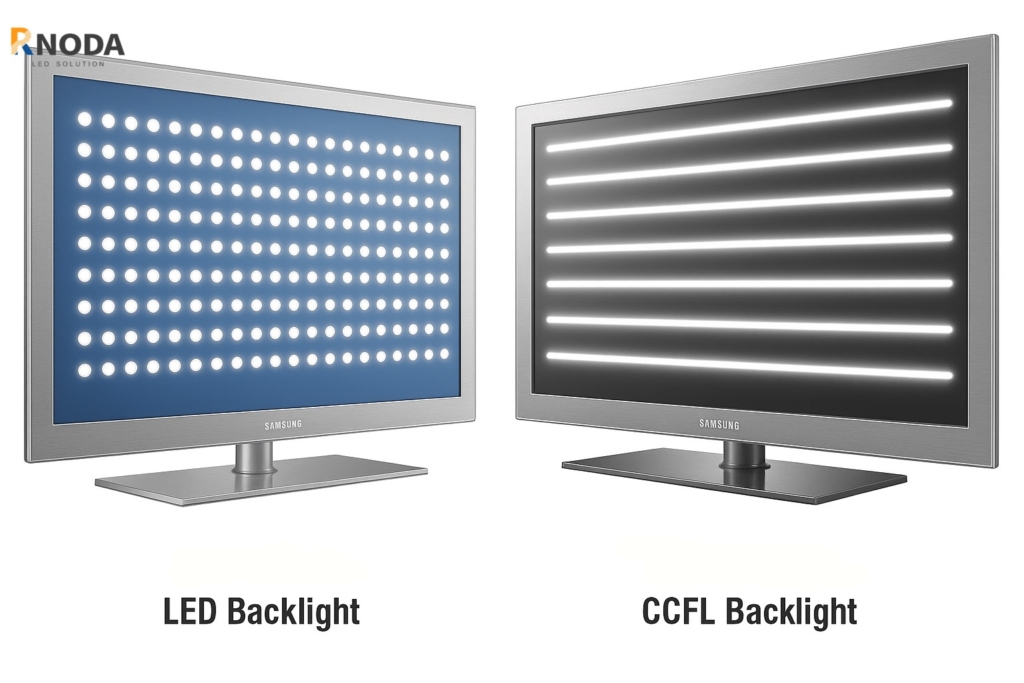
Les premiers écrans utilisaient principalement des CCFL (lampes fluorescentes à cathode froide) comme sources de rétroéclairage. Ces lampes présentent des problèmes tels qu'une consommation d'énergie élevée, une génération de chaleur élevée, une durée de vie limitée et une susceptibilité au vieillissement. De plus, pour obtenir une luminosité uniforme, il faut empiler plusieurs lampes, ce qui augmente les coûts et l'épaisseur. Les différences dans le nombre et la disposition des lampes sur les différents écrans affectent directement l'uniformité de la luminosité du rétroéclairage. Le principal avantage de ce rétroéclairage est sa luminosité élevée, il est donc largement utilisé dans les dispositifs d'affichage à cristaux liquides couleur à phase négative noir et blanc, à phase négative en mode bleu et couleur de plus grande taille. Théoriquement, il peut produire différentes couleurs sur la base du principe du mélange des couleurs en utilisant les trois couleurs primaires. Cependant, ses inconvénients incluent une consommation d'énergie élevée, la nécessité d'un circuit inverseur pour le pilotage et une plage de température de fonctionnement étroite de 0 à 60 °C, alors que d'autres sources de rétroéclairage comme les LED peuvent fonctionner entre -20 °C et 70 °C.
Applications: CCFL est principalement utilisé dans les écrans LCD de moyenne et grande taille et les équipements d'affichage industriels, et est particulièrement adapté aux applications d'affichage graphique et à haute luminosité.
| Type de source lumineuse | Avantages | Inconvénients | Applications typiques |
| DIRIGÉ | Faible coût, longue durée de vie, gradation facile | Consommation d'énergie et chaleur élevées pour les grands écrans | Écrans LCD, téléviseurs et ordinateurs portables de petite et moyenne taille |
| IL | Lumière uniforme, faible consommation d'énergie, source de lumière froide, résistante aux vibrations | Faible luminosité, courte durée de vie, léger bruit | Petits écrans LCD tels que téléphones mobiles, PDA, consoles de jeux |
| CCFL | Haute luminosité, longue durée de vie, lumière uniforme | La luminosité diminue à basse température, nécessite un inverseur, sensible aux vibrations | Écrans LCD moyens à grands, écrans graphiques |


Résumé
La sélection d'un rétroéclairage de plaque de guidage de lumière nécessite une prise en compte approfondie de la taille de l'écran, des exigences de luminosité, de la consommation électrique, de la durée de vie et du coût :
Écrans LCD petits et légers : rétroéclairage EL ou LED à éclairage périphérique
Écrans moyens à grands : rétroéclairage CCFL ou LED à éclairage direct
Écrans couleur : lumière blanche ou rétroéclairage LED RVB
 Solutions de rétroéclairage personnalisées & Fournisseur de feuilles optiques – Rnoda Tech
Solutions de rétroéclairage personnalisées & Fournisseur de feuilles optiques – Rnoda Tech


J'ai parcouru ce site Internet et je pense que vous avez beaucoup de bonnes informations, enregistrées dans les favoris (:.