In the display panel industry, optical films are the core materials that determine image brightness, uniformity, and contrast performance. With the development of LCD and OLED technologies, the roles of different types of optical films in module structures have become increasingly specialized, and they have also become key factors for panel manufacturers and material suppliers to enhance product performance.
This article will systematically explain the structural differences between LCD and OLED display modules, and focus on analyzing the types, functions, and technical challenges of common optical films, helping you understand the optical logic behind display technology.
I. The Role of Optical Films in LCD Display Modules
Overview of LCD Module Structure
An LCD display module primarily consists of two main components:
Backlight Module (BLU): Responsible for providing uniform white light
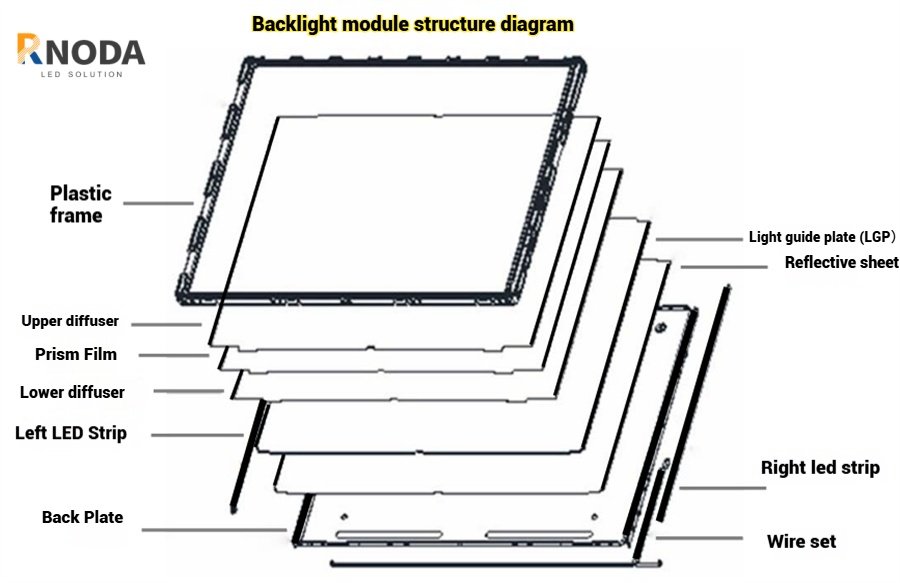
Liquid Crystal Module (LCM): Controls light transmission to achieve image display
Typical Optical Film Structure in LCD Modules:
Optical films used in the backlight module include:
Reflective Film × 1
Lower Diffusion Film × 1
Light Guide Plate (LGP) × 1
Brighteness enhancement Film (Prism Film) × 2
Upper Diffusion Film × 1
The liquid crystal panel includes the following film structures:
Polarizing film × 2 (each includes: protective film × 2 + release film × 1)
Total number of film layers: approximately 9–14 layers, with specific structures subject to minor adjustments based on design.
2. Application of Optical Films in OLED Display Modules
OLED displays have self-emitting properties and do not require a backlight module, so they use fewer optical films but have higher technical requirements.
The optical films used in OLED displays primarily include:
Circular Polarizer × 1
Includes PVA polarizing layer + TAC protective layer + adhesive layer
Release Film × 1 (for lamination)
Total number of film layers: approximately 2–3 layers
Since OLED displays prioritize contrast, anti-glare performance, and flexibility, the technical requirements for polarizing films used in OLED displays are significantly higher than those for LCDs.
3.Detailed Explanation of Major Optical Film Types and Functions
The following is a detailed description of several key optical films used in display modules:
1)Light Guide Plate (LGP)
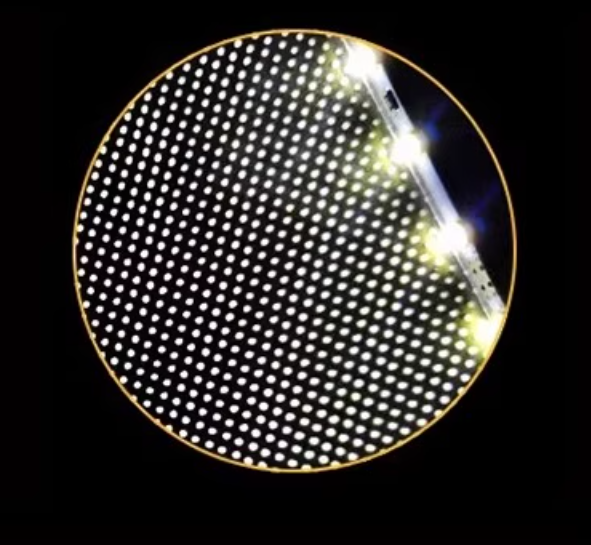
Function: Guides side light sources into the display and refracts them into a diffuse light source via a printed dot pattern on the back, achieving uniform illumination.
Material: PMMA (acrylic) or PC, suitable for laptops, light boxes, etc.
Characteristics: High light transmittance, lightweight, suitable for ultra-thin designs.
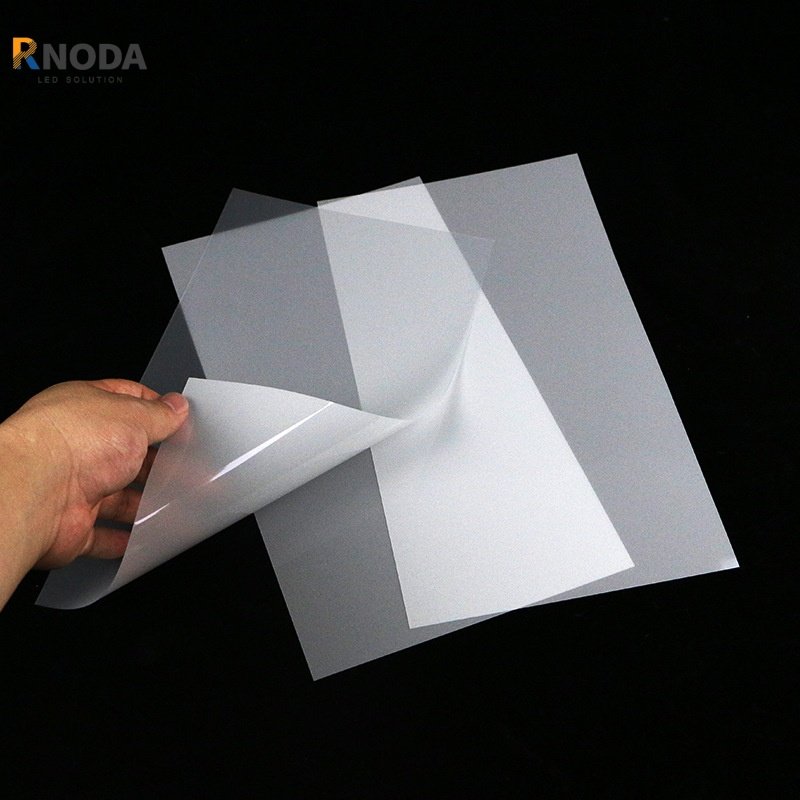
2)Reflective Film

Function: Reflects light not guided out by the light guide plate to improve light utilization efficiency.
Types:
- White Reflective Film (Coated Type, Reflectivity Approximately 95%)
- Multi-Layer Reflective Film (DBEF, Reflectivity Up to 99%-100%)
Applications: Bottom of LCD modules, reflective layer in LED lighting fixtures.
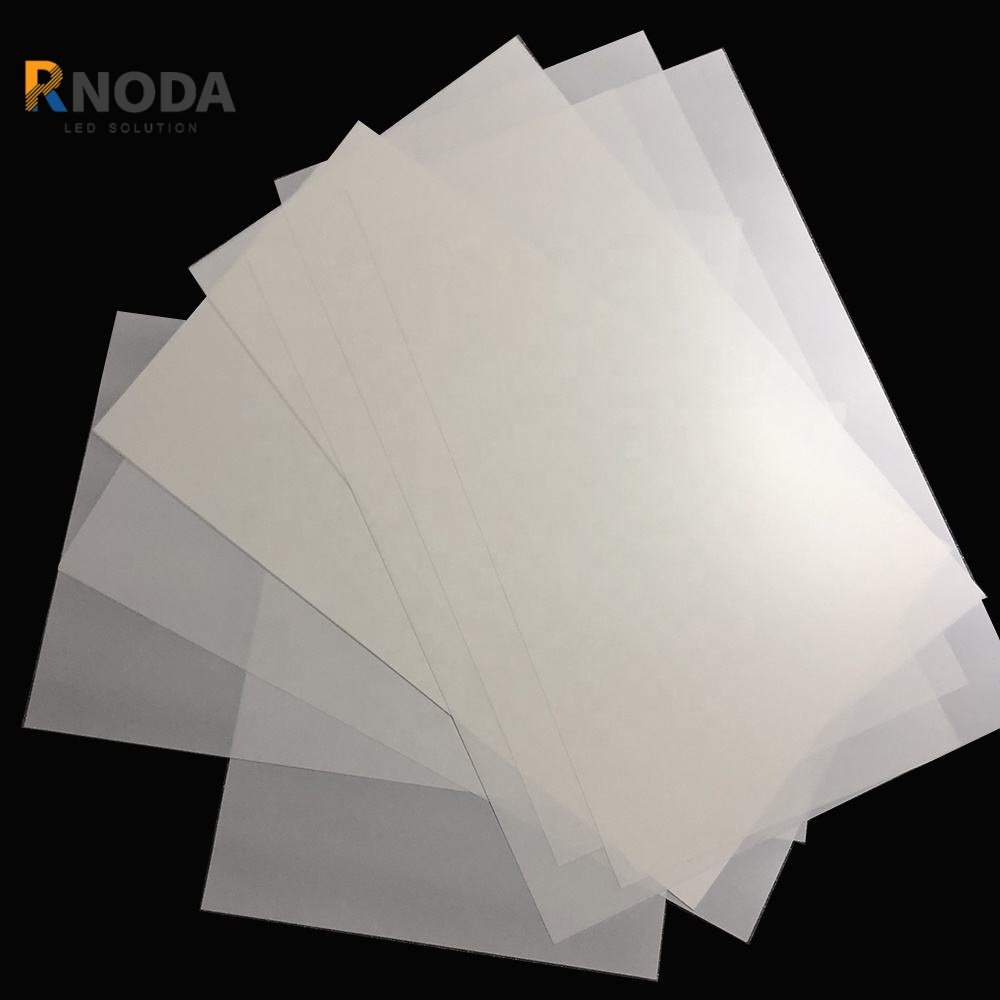
3)Diffuser Film

Function: Ensures more uniform light distribution after passing through the light guide plate, eliminates bright spots, and improves brightness consistency.
Types:
- Surface-textured type
- Internal particle-dispersed type
- Dual-sided diffuser film (balances brightness and uniformity)
Characteristics: Soft, non-glare light, enhancing the quality of the light source.
4)Brightness Enhancement Film (BEF)
Function: Guides scattered light to concentrate vertically, enhancing panel brightness when viewed directly.
Types: Common prism film, functional prism film, micro-lens film, etc.
Advantages: Can increase light efficiency by up to approximately 30%.
5)Retardation Film
Функция: Corrects the phase difference of liquid crystal molecules to improve viewing angle and contrast.
Приложение: Commonly used in IPS, VA, and other liquid crystal technologies to enhance image consistency.
6)Поляризационная пленка
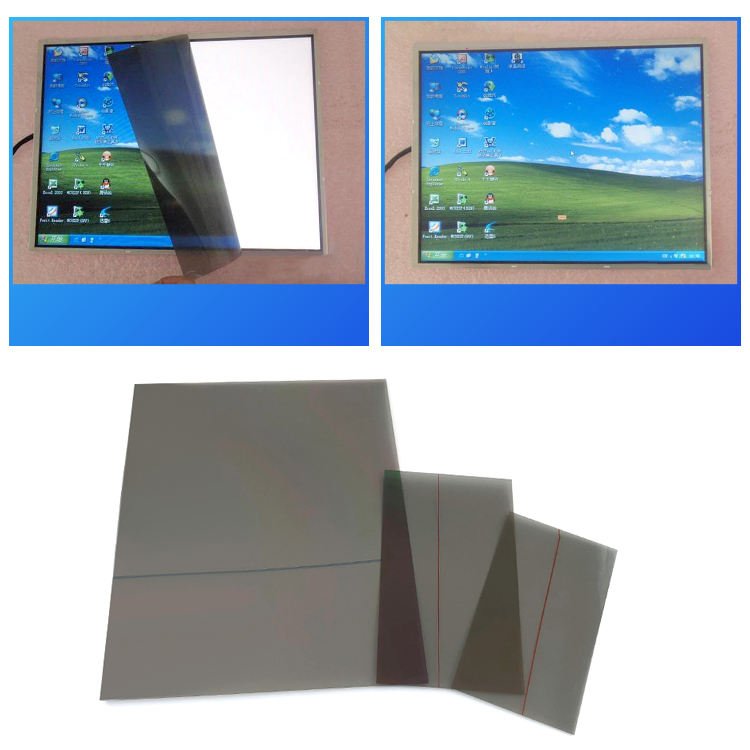

Function: Converts natural light into polarized light, working with liquid crystal molecules to control light transmission.
Composition: PVA polarizing layer + TAC protective film + adhesive layer + release film.
OLED-specific circular polarizers also feature anti-reflective functionality, making them a critical high-value-added component.
4.Future Trends: Emerging New Optical Films
New Films Function Application
Blue Light Blocking Film Filters harmful blue light Smartphones, displays
Flexible Film Bendable/rollable Foldable screens, wearables
Self-Healing Protective Film Automatically repairs scratches High-end smartphones, tablets
AF Anti-Fingerprint Film Oil-repellent and stain-resistant Touchscreens, mirror decorations
Summary
LCD Optical films, as a critical component of display modules, not only determine screen brightness, contrast, color, and viewing angle but also serve as the underlying support for the continuous upgrading of LCD and OLED technologies. Understanding the structure and functions of various films will aid in product design, material selection and procurement, customer communication, and product promotion.
 Индивидуальные решения для подсветки & Оптические листы поставщики – Rnoda Tech
Индивидуальные решения для подсветки & Оптические листы поставщики – Rnoda Tech

